The young population in Uganda especially the girl child faces many reproductive health challenges that include; high teenage unwanted pregnancies, unsafe abortions, STIs, HIV/AIDS, teenage genital mutilation, child labour, gender based violence, school dropouts all of which affect their lives.
According to the Ugandan Demographic Health Survey (UDHS) 2016, about 25% of girls aged 15-19 years have had a baby or are pregnant since the rate of pregnancy in Uganda among the adolescents stands at 24% and their sexual debut is at 16.7 years, where 15% of young girls in Uganda are married at the age of 15 and 45% by age of 18.
Uganda's HIV prevalence among the youths stands at 7.4% with 25% of all new infections occurring among the same age bracket. These challenges expose the youth to health risks hindering the achievement of national global health commitments. Adolescent girls have not received the attention they deserve as individuals, they have not been provided with the support the need to overcome inequalities, violence and discrimination that deprive them from a fair chance in life.
Some are excluded from quality education and many do not receive information about puberty and reproductive health, others are subjected to child marriage female genital mutilation, sexually transmitted diseases and gender based violence all of which have lifelong consequences.
The vulnerable index for youths especially girls indicates that while all adolescents are entitled to descent livelihoods, girls face disproportionate risks and distinctive consequences from the vulnerabilities experienced. A big number of them in schools and at homes have not gained comprehensive information concerning their health rights, sexuality, HIV/AIDS or sexual education by both teachers and their parents thus making or leading the girls coming up with uniformed decisions about their sexuality and interpersonal relationships.
The above statistics show that adolescent girls are the most vulnerable.


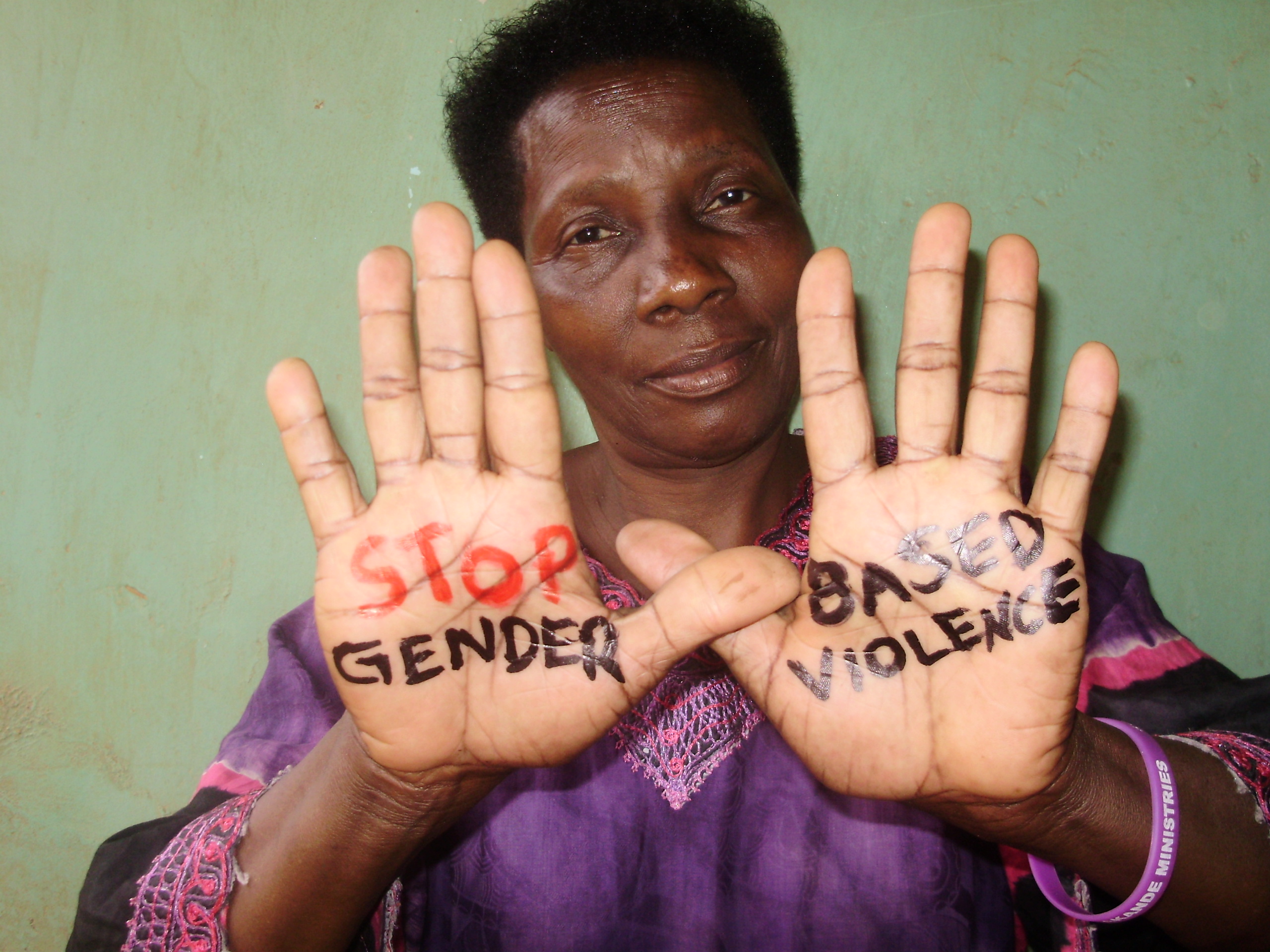







Comments